DRIPPER TECHNICAL TCE
📄 Technical Data Sheet – Irrigation Dripper
1. Product Description
A dripper, also known as an emitter, is a small-flow device used to deliver controlled amounts of water directly to the plant root zone in drip irrigation systems.
2. Emitter Types
Non-Pressure-Compensating (NPC): Flow varies with pressure changes (exponent x ~0.4–0.8)
Pressure-Compensating (PC): Maintains nearly constant flow across a range of pressures (x ≈ 0)
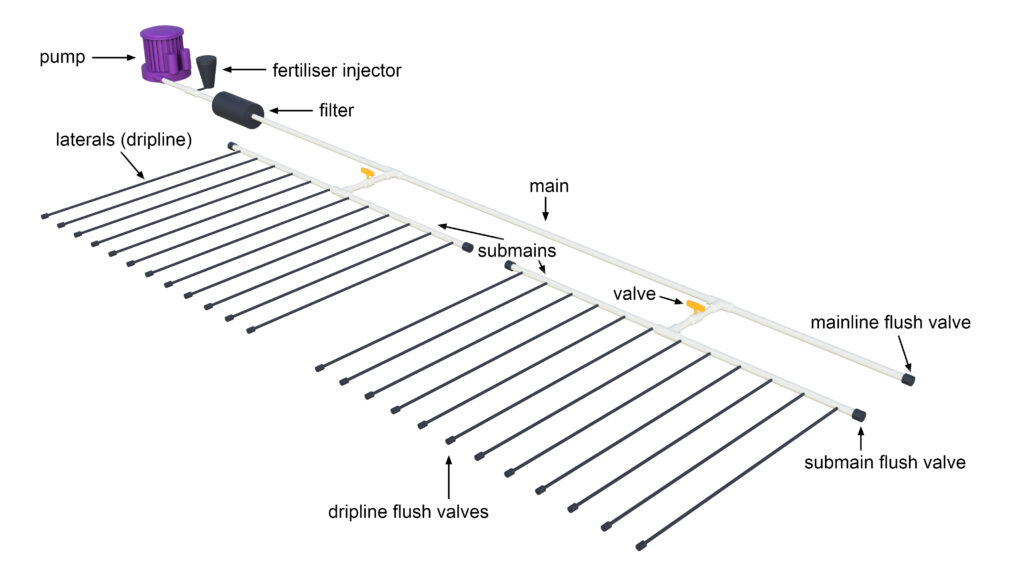
Inline Dripper Tube: Emitters molded into drip tubing at set intervals
3. Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Typical Values / Range |
|---|---|
| Flow Rate | 0.2 – 4.0 L/h |
| Nominal Operating Pressure | 0.5 – 5.0 bar (PC) |
| Emitter Discharge Exponent (x) | 0.4–0.8 for NPC; ≈0 for PC |
| Spacing | 20 – 100 cm depending on soil & emitter flow |
| Lateral Length (max) | 20 mm tube – up to ~331 m for 4 L/h @ 2.5 bar |
| Tubing Inner Diameter | 11.4 – 21.0 mm |
| Wall Thickness | 0.2 – 1.2 mm |
4. Design Features
Flow Path Geometry: Turbulent flow through labyrinth channels to resist clogging
Pressure Regulation: PC models include flexible diaphragms for stable flow
Anti-Siphon Valve (optional): Prevents dirt suction when line pressure drops
Self-Cleaning Channels: Short wide passages promote flushing during operation
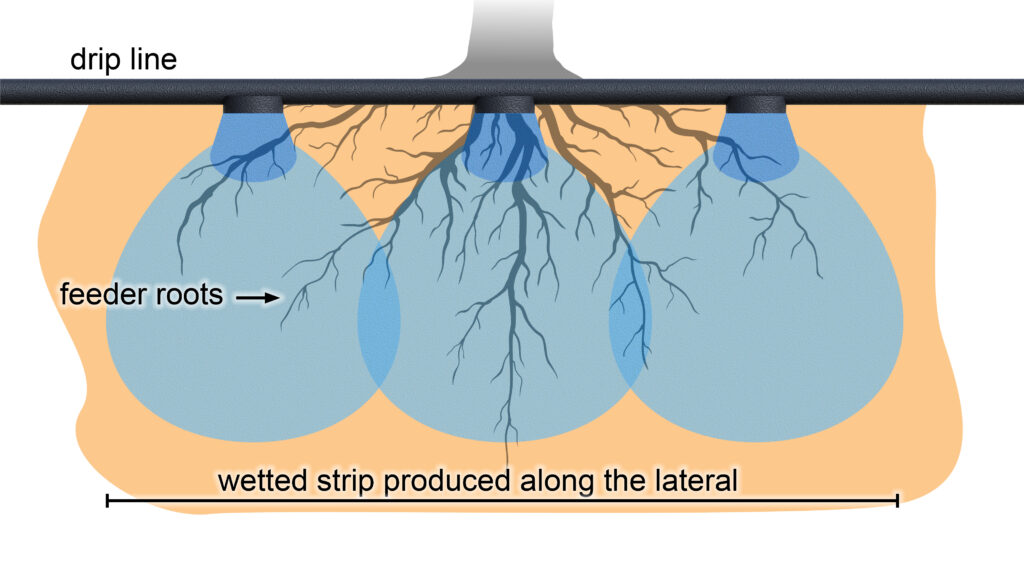
5. Applications & Soil Considerations
Soil Type Effect:
Clay: Wide, shallow wetting requiring moderate flow & long durations
Sandy: Deep, narrow wetting needing higher flow or close spacing
Flow & Spacing Design: Flow rate × spacing determines water application rate (mm/h).
Emitter Counts: Use flow rate ratings (e.g., 0.5–2 GPH) to size system
Maximum Lateral Length: Defined per tubing specs and desired pressure loss
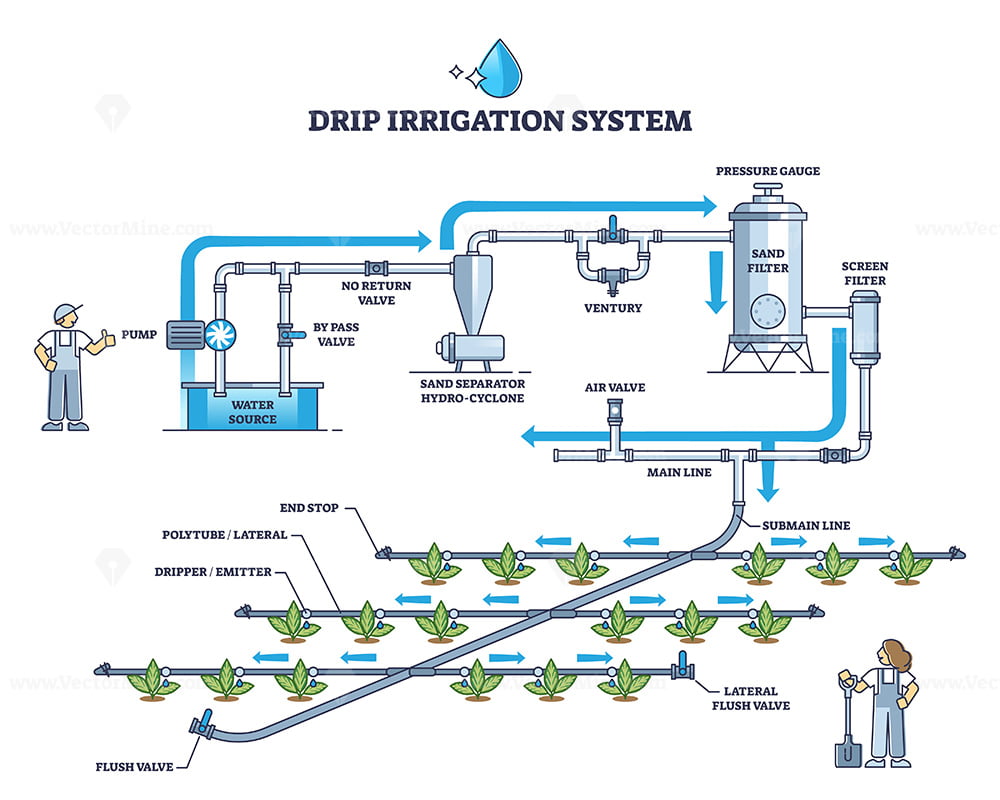
6. Installation Guidelines
Use clean, well-filtered water (80–200 mesh filters) to prevent clogging
Maintain operating pressure within rated range
Flush lines before planting
Match emitter spacing & flow to soil and crop needs
Monitor pressure loss and water distribution uniformity
Clean filters backflush regularly
7. Advantages
High water-use efficiency (>90%)
Precise delivery reduces waste and runoff
Modular and scalable design
Pressure compensating types offer uniform irrigation even on slopes